-
 Non-fluorescent(Raman) Calcium Fluoride
Non-fluorescent(Raman) Calcium FluorideCalcium fluoride itself is also called fluorite, so non-fluorescence is only a relative concept, while most are also called Raman grade calcium fluoride, and the wavelength of the material applied and the laser energy are directly related, for example, 450NM non-fluorescence does not mean 355NM non-fluorescence, 2W laser non-fluorescence does not mean 5W laser non-fluorescence. Fluorescence can cause strong absorption, resulting in energy loss, signal distortion or imaging disturbances. Fluorescence is produced on the one hand by the elemental composition of the crystal material itself and also by defects created during the growth of the material. Therefore, fluorescent products are either selected materials or custom-made products, which are monitored by fluorescence spectrometers, energy spectrometers or extreme ultraviolet irradiation and are relatively expensive.
-
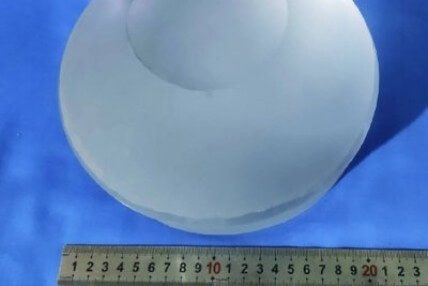 Large size Calcium Fluoride
Large size Calcium FluorideCalcium fluoride is used for the development or bulk requirements of polycrystalline materials over 150 mm and single crystals over 120 mm.
These products are mostly used in astronomical observation, high-altitude imaging, satellite communications, public safety and high-energy laser transmission.
They require high stress and uniformity in the material itself, as well as high precision in the processing of the material, and are mostly recommended for CNC or DTM processing.
If openings and special shapes are involved, it is recommended to provide requirements for material stress.
-
 UV vacuum Calcium Fluoride
UV vacuum Calcium FluorideIt should be used in the wavelength range 130-200NM, sometimes up to 110NM.
The material is mostly used in UV spectral analysis and in KF/CF vacuum windows, requiring high transmittance and good irradiation resistance below 200NM.
Vacuum grade calcium fluoride requires high purity of the raw material and control of the mixing of other elements in the crystal growth process, and try to improve the transmittance below 200 NM.
-
 Excimer Calcium Fluoride
Excimer Calcium Fluoridefor use on lasers in the 193/248/366NM wavelength band.
Can be used as a laser light source, lighting equipment and imaging equipment, where the light source requirements mainly require high internal transmittance, no colour core, laser damage threshold to be good, so that the life of the light source can be greatly extended; laser external light path system on the material uniformity and consistency requirements are higher, at the same time because of the ultra-precision characteristics of the workpiece, the material often requires precision annealing, all the excimer grade materials are All excimer grade materials are custom-made products, which are the high-end products in calcium fluoride materials.
Calcium fluoride belongs to the cubic crystal system of the high-grade crystal family and is typically isotropic.
However, this is often only theoretical. In practical applications in complex and high-precision optoelectronic systems or for high-power laser purposes,
or in applications such as gyroscopes and high-precision microscope lenses, calcium fluoride in specific orientations is often the preferred solution for optical designers and applicators,
based on the nuances of the material and the cumulative errors in material processing.
-
 UV Calcium Fluoride
UV Calcium FluorideTypical spectral characteristics are 205NM and 306NM with no significant absorption, and the requirement for no reduction in infrared transmission. UV single crystals are mostly used in day-blind detectors 260-280NM or for UV imaging to eliminate chromatic aberrations, resulting in lower noise and better image quality. They are also partially used in UV vacuum observation windows or for spectral analysis. UV materials are mostly high purity chemical synthetics and require controlled absorption of cerium and lead in the crystal growth and must comply with ROHS & REACH standards. There are, of course, some natural ore materials that are screened later to meet the requirements, but because the consistency and stability of the material is not guaranteed, natural materials are generally not recommended.
-
 Infrared polycrystalline Calcium Fluoride
Infrared polycrystalline Calcium FluorideIR polycrystalline, a structure with multiple crystals applied beyond 400 NM.
The typical characteristic is the presence of distinct grain boundaries, the number of grain boundaries is greater than one, mostly between two and four, and the number is not controllable.
The permeability of polycrystals is the same as that of single crystals, the chemical properties are the same and the physical mechanical properties are not significantly different from those of single crystals, but the optical delay properties are not as good as those of single crystals.
Because of the homogeneous properties of calcium fluoride and the high yield and low price of polycrystals, they can be used for protective windows, single lenses or single prisms, but for high power laser applications or for lenses in a set, single crystals are often recommended.
- Crystal Material
- Lanthanum tribromide LaBr3
- Calcium fluoride (CaF2)
- Barium fluoride(BaF2)
- Magnesium fluoride (MgF2)
- Lithium fluoride(LiF)
- Silicon material(Si)
- Germanium material(Ge)
- NaI:TI
- Lithium Niobate
- Zinc Selenide(ZnSe)
- Zinc Sulfide(ZnS)
- Sapphire
- Quartz
- Laser Lenses
- Laser output Coupler
- Laser Protection Window
- Beam Combine
- Laser scanning mirror
- Laser Mirror
- Focusing Lens
- Laser Window